Congratulations to the team members for this new article about “Species-specific regulation of XIST by the JPX/FTX orthologs” published in Nucleic Acids Research (Feb 2023).
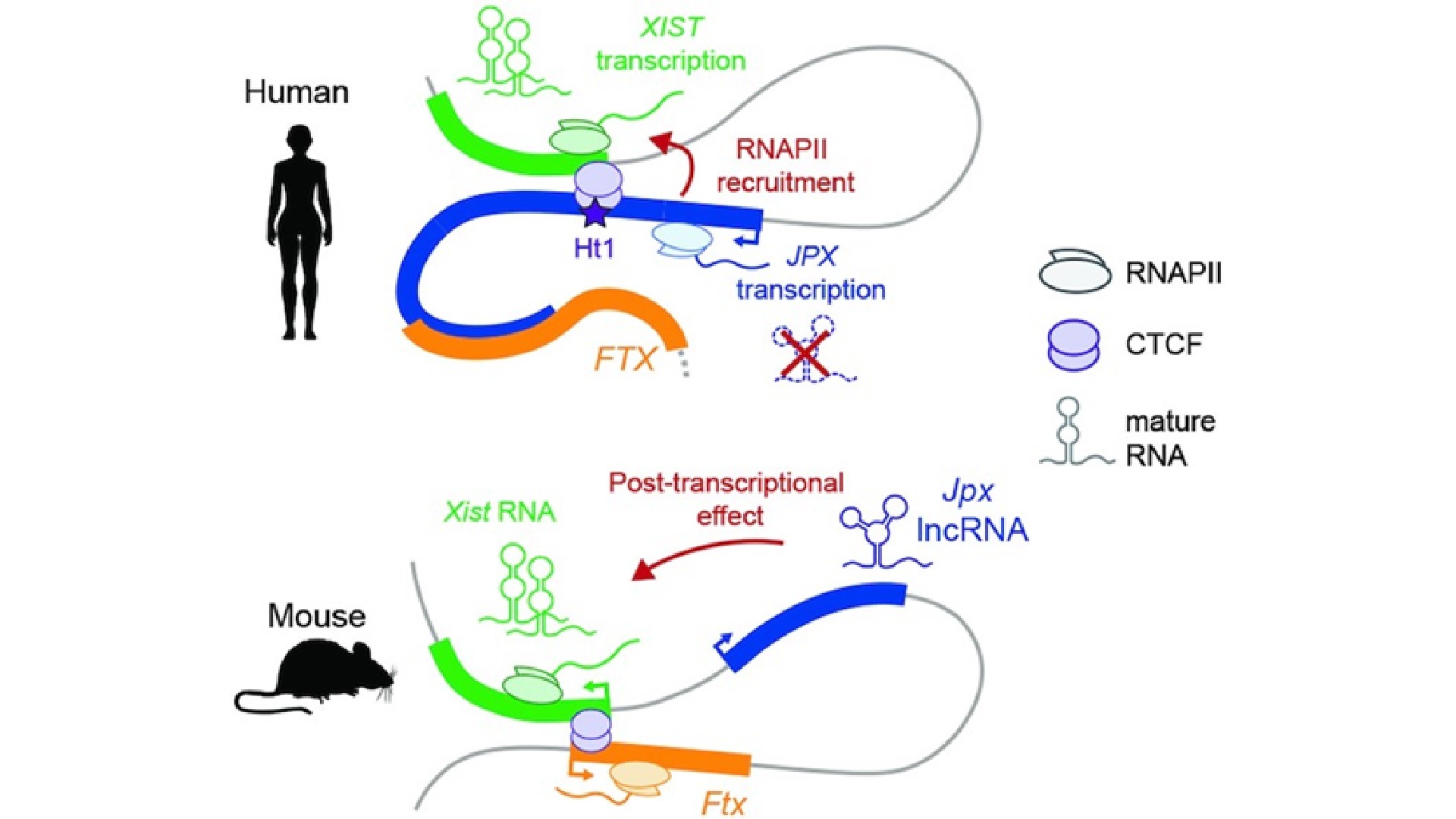
Graphical abstract
In contrast to the mouse, human JPX regulates XIST through mechanisms that are independent of JPX mature transcript, but which involve JPX transcription.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Species-specific regulation of XIST by the JPX/FTX orthologs.
Rosspopoff O, Cazottes E, Huret C, Loda A, Collier AJ, Casanova M, Rugg-Gunn PJ, Heard E, Ouimette JF, Rougeulle C. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Feb 2:gkad029. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad029.
Read more
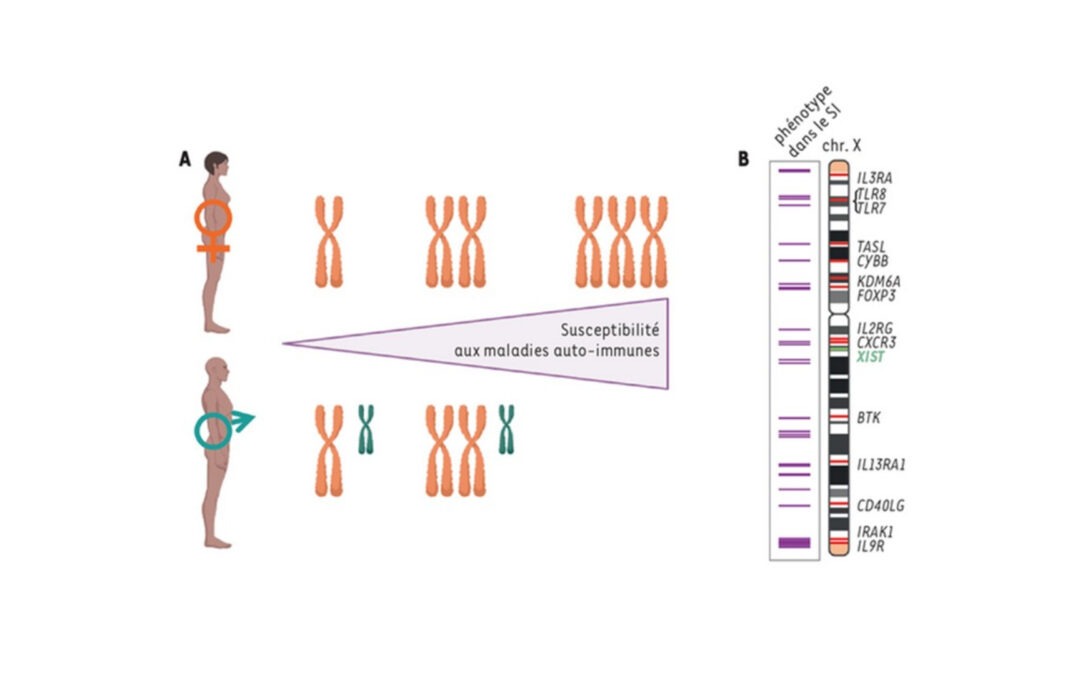
New review: X chromosome regulation and female functional specificities: Are two Xs better than one?
What if the presence of two X chromosomes confers functional specificities on female cells and contributes to the different susceptibilites of men and women to certain diseases? One of the X chromosomes is randomly silenced in each female cell from the embryonic...
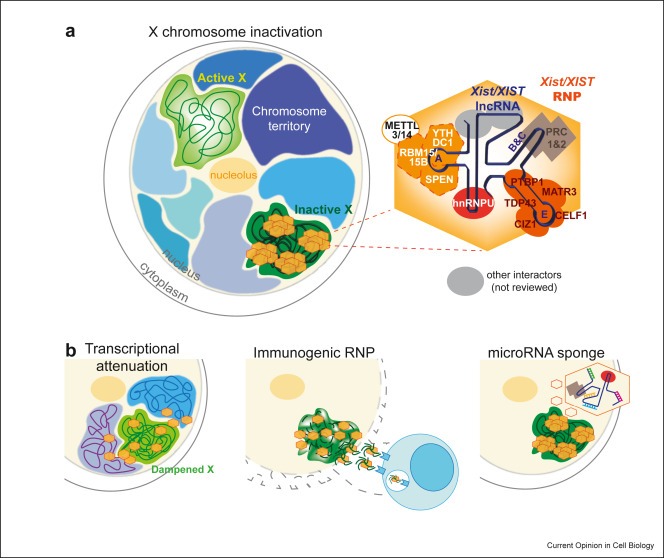
New review: Unleashing XIST from X-chromosome inactivation
The discovery that long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are the most abundant gene class in the human genome has sparked significant research, particularly on Xist, a key RNA involved in X-chromosome inactivation. Recent studies have expanded our understanding of Xist's...

Congratulations Dr Carrillo
Congratulations to Léo who defended his thesis work on " Exploring the link between X chromosome inactivation and the development of human extraembryonic tissues " . © Rougeulle team À lire aussi
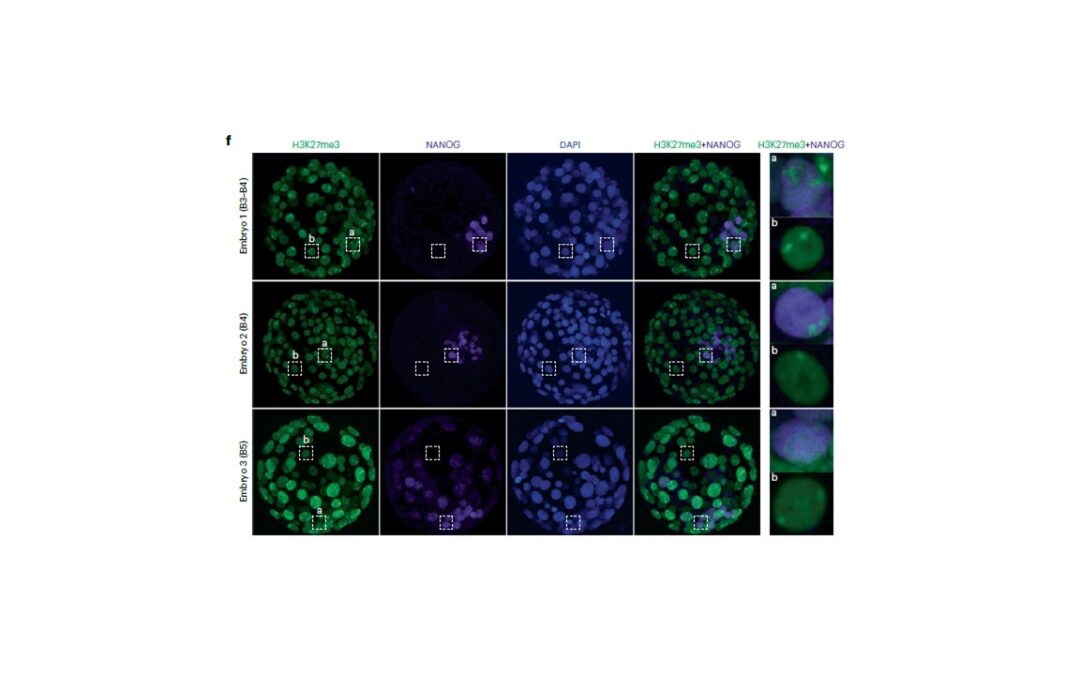
Article: XIST dampens X chromosome activity in a SPEN-dependent manner during early human development
Our latest work carried out by Alfeghaly C. et al. elucidating the mechanism of dampening of X-linked gene expression during pre-implantation development. To discover the role of the long non-coding RNA XIST and its particular partner SPEN click on the link: Nature...
