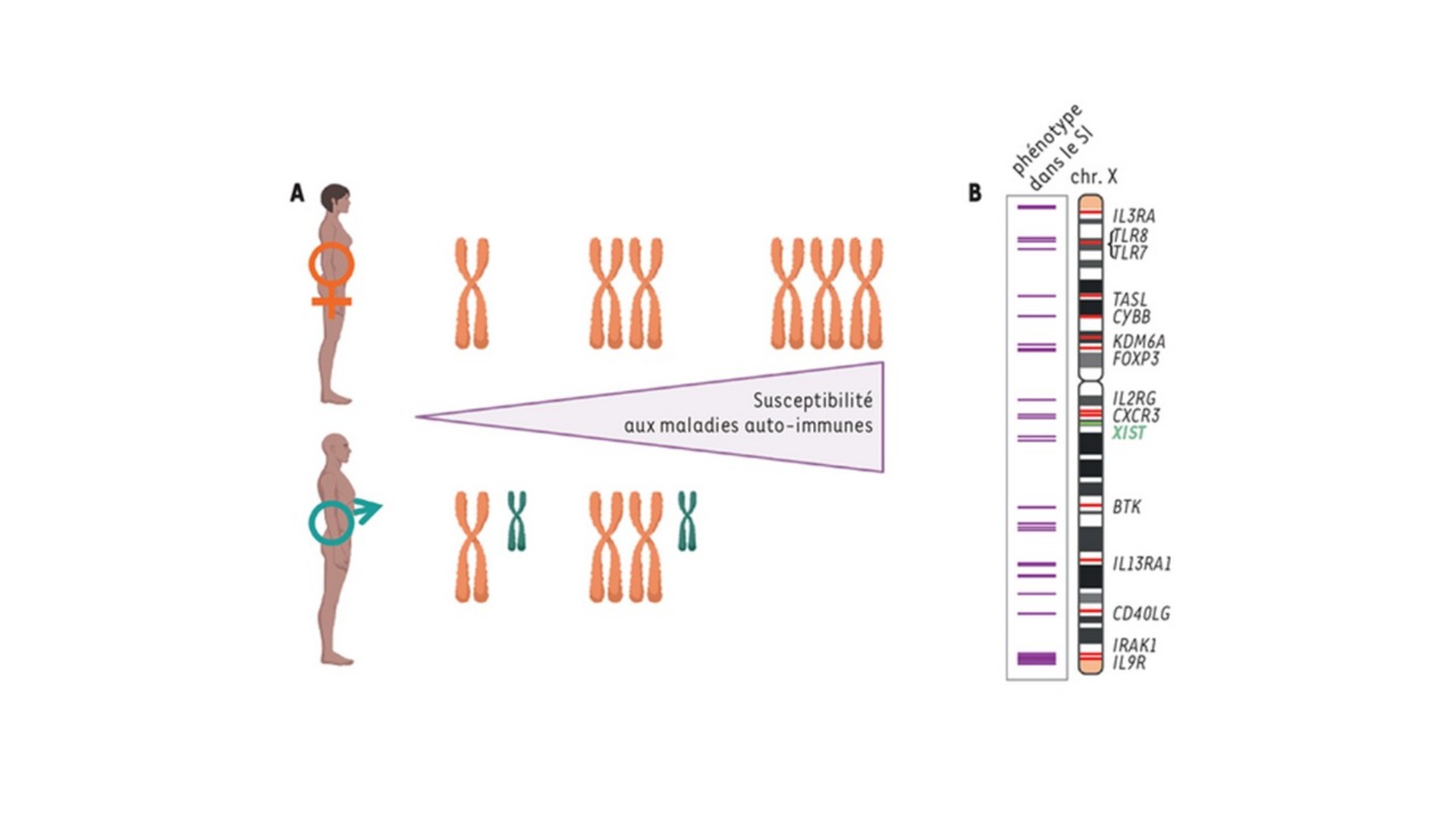
What if the presence of two X chromosomes confers functional specificities on female cells and contributes to the different susceptibilites of men and women to certain diseases? One of the X chromosomes is randomly silenced in each female cell from the embryonic stage, theoretically making the sexes equal. This silencing of the X chromosome is a unique epigenetic process, affecting an entire chromosome and resulting in mosaic expression of X-linked genes throughout the body. However, some genes escape this process and X-inactivation appears to be somewhat labile in certain cell types. What are the physiological implications of these observations? This question is beginning to be explored, particularly in the immune and nervous systems, where several pathologies have sexual bias.
https://www.medecinesciences.org/fr/articles/medsci/full_html/2024/11/msc240158/msc240158.html
Medecine Sciences ©
À lire aussi

Welcome to Léa
Léa joins the team as a research assistant. After completing a master's degree in virology, she worked in Strasbourg on grapevine viruses, then on characterizing mRNA degradation in plants at the Institute of Plant Molecular Biology (IBMP). In the Polo team, Léa will...

Sophie Polo receives an Impulscience® grant from the Fondation Bettencourt Schueller
Sophie Polo has been awarded an Impulscience® grant to fund a research project on the establishment and maintenance of the inactive X chromosome in response to DNA breaks. This is wonderful news for the lab ! We thank the Fondation Bettencourt Schueller for their...

Welcome to Léa, new engineer in the team!
Léa joins the lab as a research assistant. She holds a Master's degree in Molecular and Cellular Biology from Sorbonne University. She will contribute to investigate DNA methylation maintenance mechanisms in response to UV damage in mammalian cells. Léa Girard À lire...

Well done, Dr Mori!
Margherita successfully defended her PhD on DNA methylation maintenance in response to UV damage. Brava! Margherita and her thesis jury. From left to right: Sophie Polo, Sandra Duharcourt (on screen), Déborah Bourc'his, Margherita Mori, Nataliya Petryk, Jean Molinier,...
